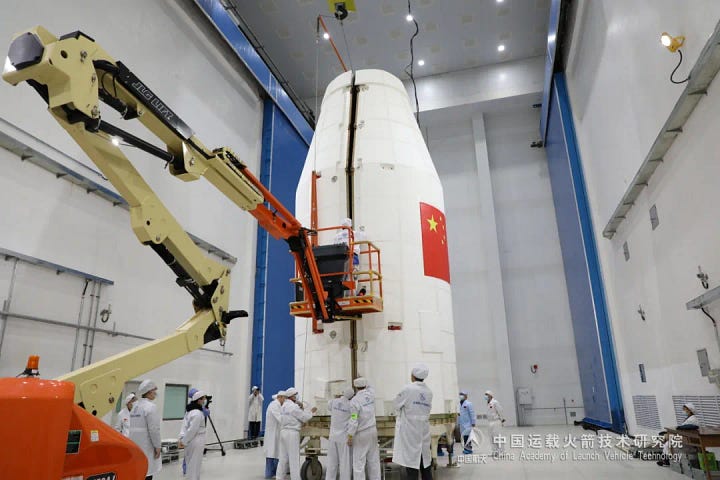
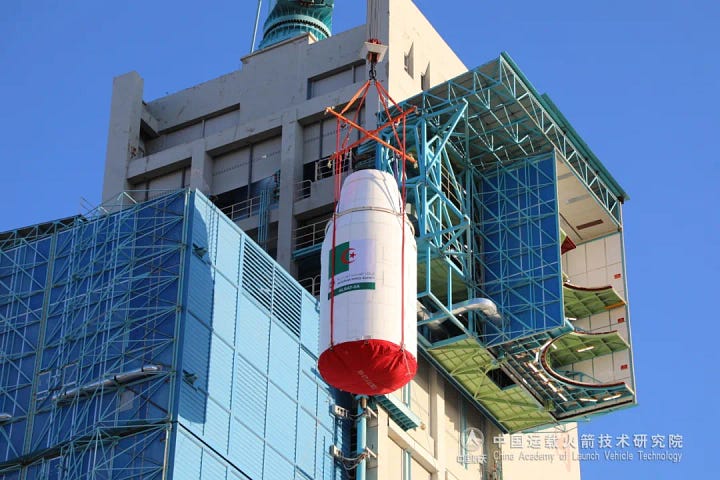
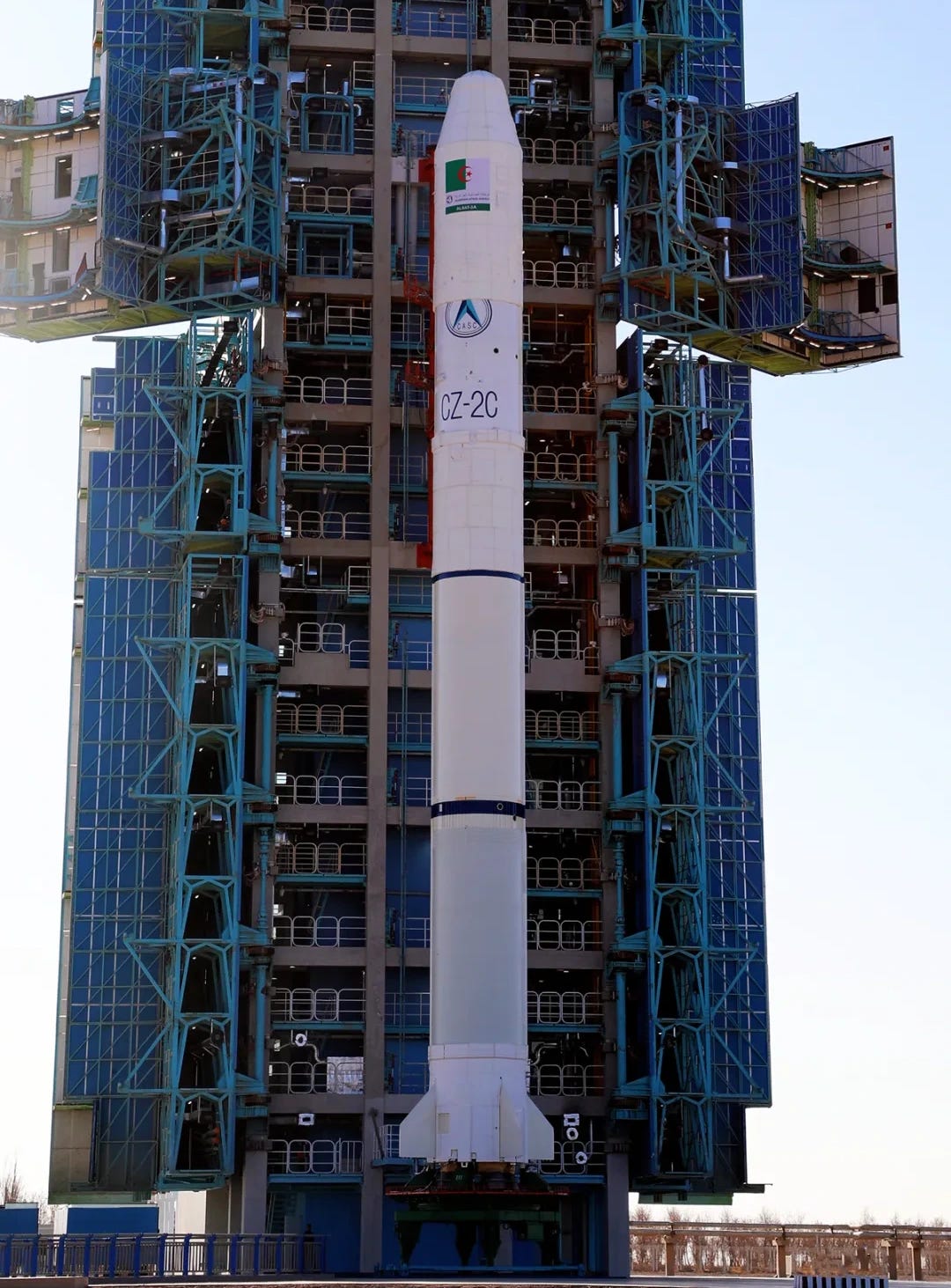
Algerian Remote Sensing Satellite Delivered to Orbit From Jiuquan [Long March 2C]
China’s space enterprises have supported their first launch for an international customer this year.
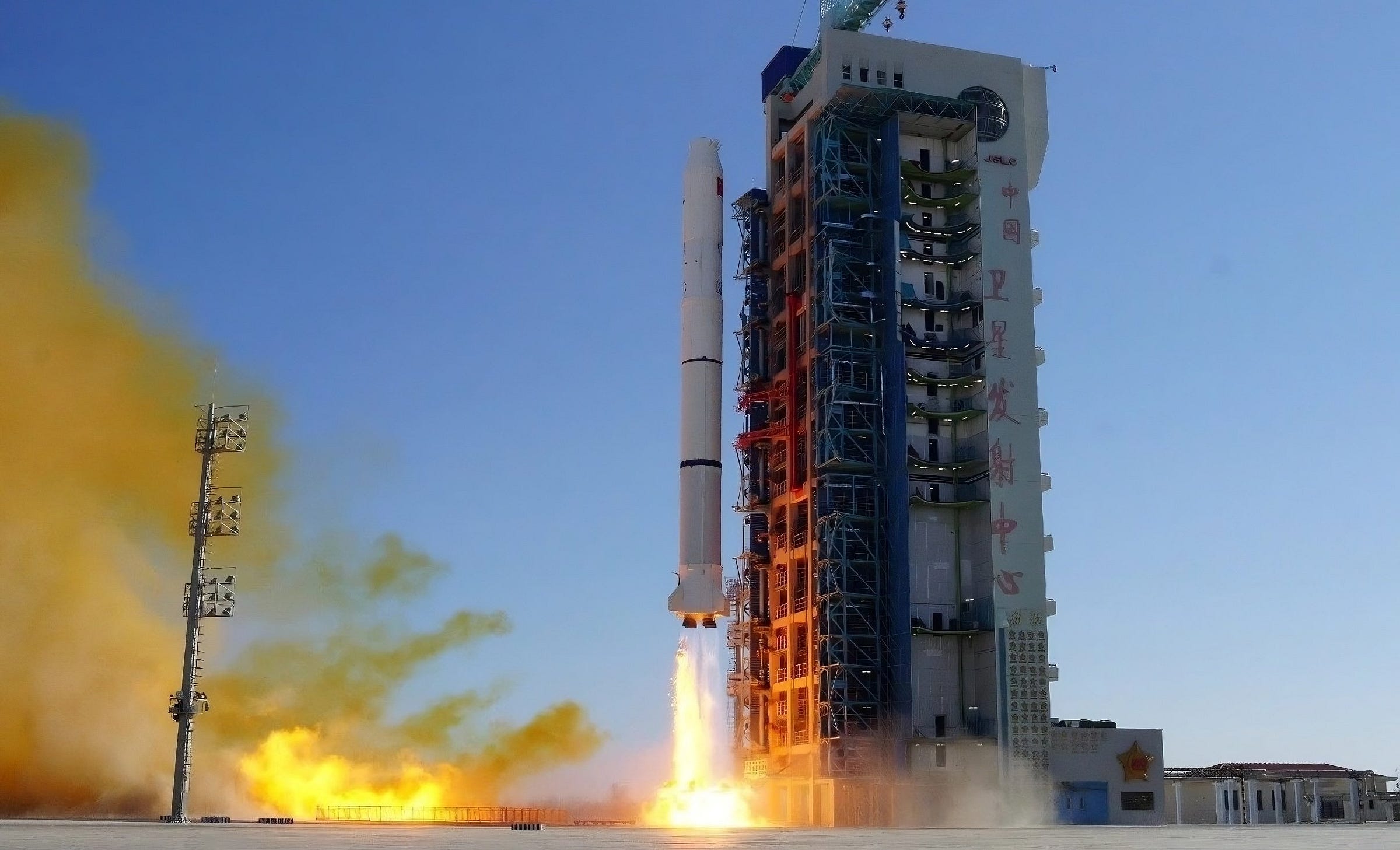

Off of Launch Site 94 at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, a Long March 2C lifted off at 12:01 pm China Standard Time (04:01 am Universal Coordinated Time) on January 15th, heading toward sun-synchronous orbit on behalf of an international customer.
That customer was the Algerian Space Agency with AlSat-3A (阿尔及利亚遥感三号A), developed by the China Academy of Space Technology through China Great Wall Industry Corporation. AlSat-3A is the first of two Chinese-made remote sensing satellites, signed for in July 2023, for the North African country, with them primarily set to support land-use planning as well as to enhance capabilities for disaster prevention and mitigation.
The deployment of AlSat-3A and the coming launch of AlSat-3B in the future are under the second Algeria-China Strategic Cooperation Plan (2022-2026), with space being one of the key cooperation areas. China’s state-owned space enterprises supporting today’s launch hailed it as an example of the One Belt, One Road Initiative’s (一带一路) cooperation, which Algeria is part of.
Back in December 2017, China launched Algeria’s first communications satellite, Alcomsat-1, towards geostationary space, which has since improved the country’s standard of living by connecting thousands of schools and hospitals, alongside training over three hundred Algerian technicians to operate it.
Once the successful completion of the Long March 2C’s first flight of the year was confirmed, the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology stated that this is the first of several in 2026 for a period of high-density launches. It was also shared that additional air conditioning systems were attached to several of the launch vehicles’ systems to deal with Jiuquan’s high temperature and humidity during the launch campaign.
Today’s launch was the 85th launch of the Long March 2C, and the 626th launch of the Long March launch vehicle series. This was also the 3rd launch from China in 2026.
Liftoff video via 我们的太空 and 大漠问天 on WeChat.
Check out the previous Long March 2C launch
What is the Long March 2C?
This section is for those less familiar with China’s Long March series of launch vehicles.
The Long March 2C is one of the oldest launch vehicles from China performing missions regularly to low earth and sun-synchronous orbits by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology. The two stages of the launch vehicle both burn Dinitrogen Tetroxide and Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine.
The payload capacity of the launch vehicle is currently as follows:
3,850 kilograms to low Earth orbit
1,900 kilograms to a sun-synchronous orbit
1,250 kilograms to a geostationary transfer orbit
The first-stage is powered by four YF-21C engines, which generate 302 tons of thrust burning Dinitrogen Tetroxide and Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine. The second-stage is powered by a single YF-22E engine and four YF-23C verniers that generate 80 tons of thrust while also burning Dinitrogen Tetroxide and Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine.
On the launch pad, the Long March 2C is 42 meters tall and weighs 233,000 kilograms when fully fuelled. The first and second stages have a diameter of 3.35 meters, with the fairing having a diameter of either 3.35 or 4.2 meters.
So far the Long March 2C has flown from all three inland launch sites, the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center, and the Xichang Satellite Launch Center.





