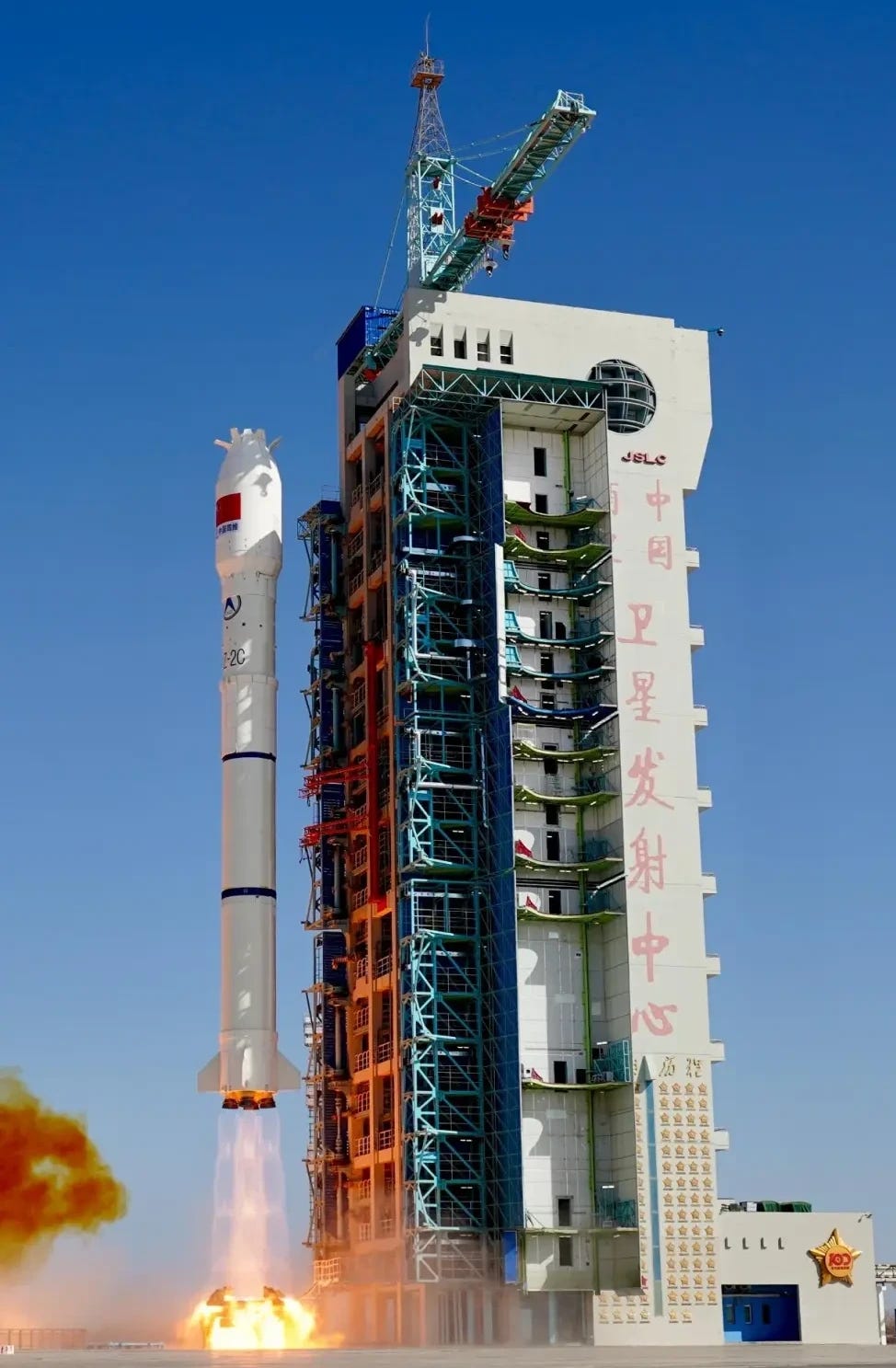
New High-Quality Commercial Imaging Satellites Launched [Long March 2C Y81]
China Siwei Survey and Mapping Technology has two new industry leading satellites in orbit.
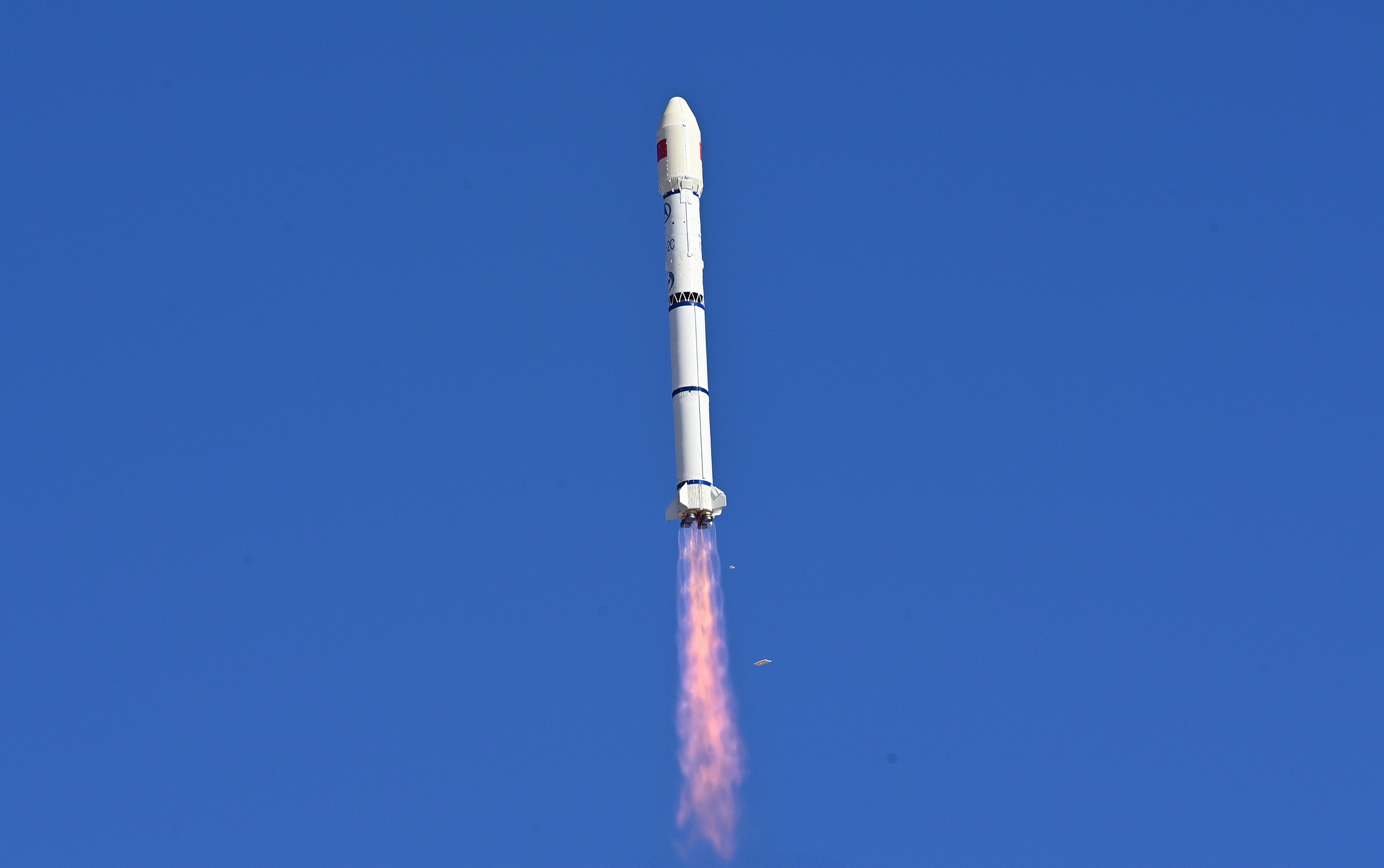

At 15:08 pm China Standard Time, or 07:08 Universal Coordinated Time, on February 27th a Long March 2C lifted off from Launch Area 4 at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, heading for sun-synchronous orbit. Riding atop of the rocket were two new commercial imaging satellites.
Those two satellites were Siwei Gaojing-1 03 (四维高景一号03) and Siwei Gaojing-1 04 (四维高景一号04), also referred to as SuperView Neo-1 03 and 04 in English. These satellites are planned to be operated by China Siwei Survey and Mapping Technology (中国四维测绘技术有限公司). Both satellites were developed and manufactured by the Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology.
Siwei Gaojing-1 03 and 04 are claimed to be China’s highest-resolution commercial remote sensing satellites with the characteristics of ultra-high resolution imaging, high positioning agility and accuracy, as well as high capacity storage with high-performance digital transmission capabilities. The Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology expands on these characteristics:
“Ultra-high resolution imaging: the satellite adopts the "dynamic and static separation" dual-super technology of the Eighth Academy, and is equipped with a large-aperture optical camera "magnetically suspended" on the satellite platform, achieving ultra-precise and ultra-stable high-definition "anti-shake imaging". It has the highest imaging resolution among domestic commercial remote sensing satellites and is a space "clairvoyant" with accurate pointing and clear vision. With ultra-high agility control, the satellite applies dual ultra-agile control technology in orbit for the first time, which enables the satellite to realize a variety of flexible imaging modes such as push-sweep imaging, multi-point agility imaging, multi-band splicing imaging, stereoscopic imaging, and curve track imaging, etc., so that the satellite can respond to users' various needs quickly, and it is a genuine “versatile hand” for space-to-Earth remote sensing. Ultra-high positioning accuracy: the satellite first applied the angle monitoring technology in the domestic commercial remote sensing field, and established a "goniometer" with a sub-arcsecond accuracy between the camera pointing and the platform attitude reference, and monitored the slight changes in the angle caused by factors such as thermal deformation in space in real-time on orbit, achieving an image positioning accuracy of better than 5 meters without ground control points, reaching the world's advanced level of commercial satellites.”
If there are any problems with this translation please reach out and correct me.
Once the two satellites are commissioned, they will provide imaging for various fields including natural resource monitoring, urban safety planning, emergency management and response, as well as for maritime affairs. The two new satellites launched today are also expected to work with China Siwei Survey and Mapping Technology’s other satellites, including four satellites launched in November.

In its post-launch blog post, the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology highlighted that it has been flying the Long March 2C for almost forty-three years, delivering payloads to low Earth orbit and all the way out to geostationary transfer orbits. The academy also stated that today’s launch continued to prove the launch vehicle’s reliability and mission flexibility.
Today’s launch was the 82nd launch of the Long March 2C, and was the 561st launch of the Long March launch vehicle series. This was also the 9th launch from China in 2025.
Liftoff video via 小陵气象航天时间, 北京蓝龙, 空天逐梦, and 中国四维 on Weibo.
Check out the previous Long March 2C launch
What is the Long March 2C?
This section is for those less familiar with China's Long March series of launch vehicles.
The Long March 2C is one of the oldest launch vehicles from China performing missions regularly to low earth and sun-synchronous orbits by the China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology. The two stages of the launch vehicle both burn Dinitrogen Tetroxide and Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine.
The payload capacity of the launch vehicle is currently as follows:
3,850 kilograms to low Earth orbit
1,900 kilograms to a sun-synchronous orbit
1,250 kilograms to a geostationary transfer orbit
The first-stage is powered by four YF-21C engines, which generate 302 tons of thrust burning Dinitrogen Tetroxide and Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine. The second-stage is powered by a single YF-22E engine and four YF-23C verniers that generate 80 tons of thrust while also burning Dinitrogen Tetroxide and Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine.
On the launch pad, the Long March 2C is 42 meters tall and weighs 233,000 kilograms when fully fuelled. The first and second stages have a diameter of 3.35 meters, with the fairing having a diameter of either 3.35 or 4.2 meters.
So far the Long March 2C has flown from all three inland launch sites, the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center, and the Xichang Satellite Launch Center.